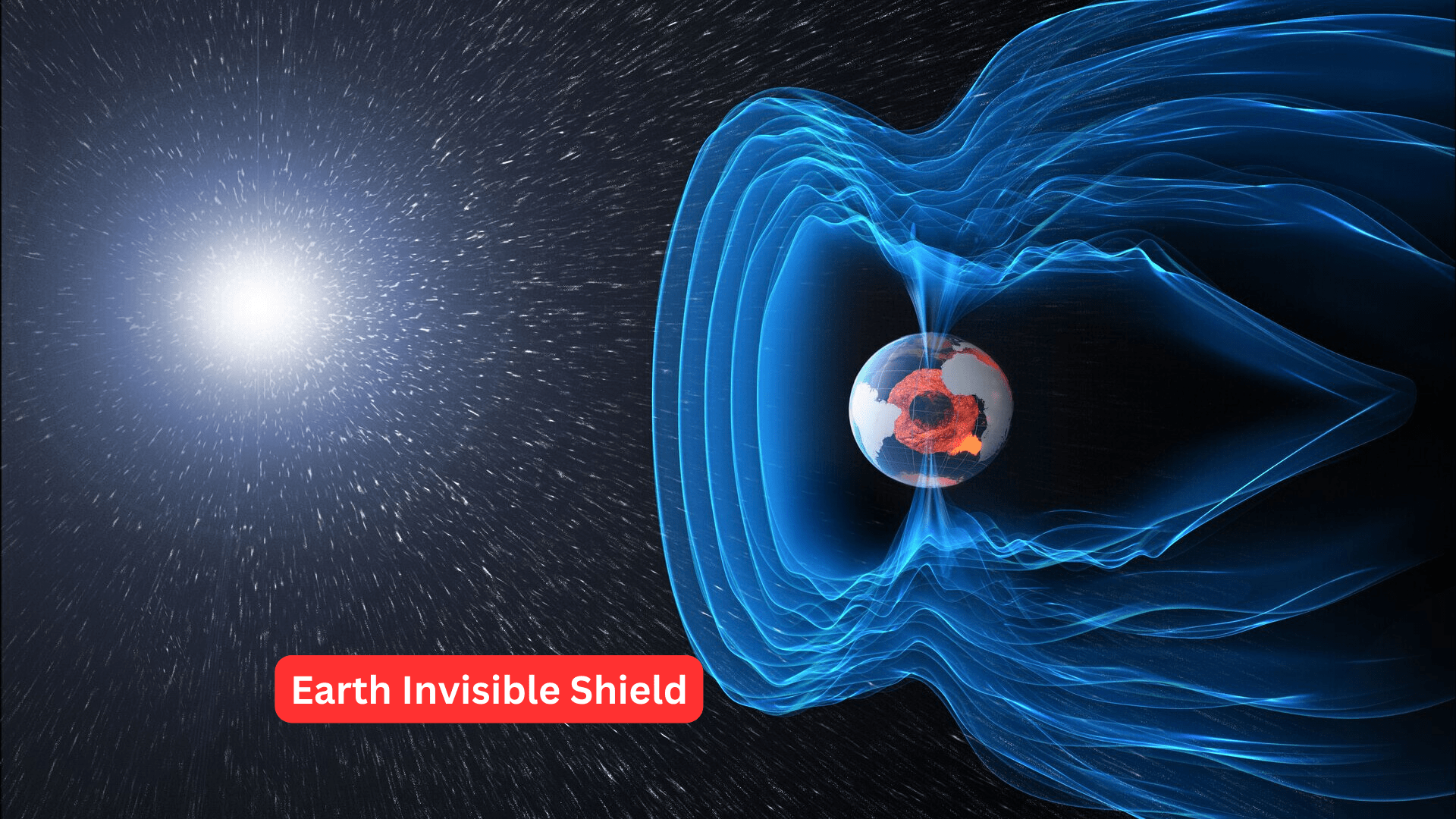
The Earth, a dynamic and complex celestial body, harbors various layers of protection that safeguard its inhabitants and influence its long-term evolution. While the term “invisible shield” may evoke imagery of a sci-fi force field, it is grounded in the scientific realities of Earth’s natural defenses. These shields, comprising magnetic fields, atmospheric layers, and protective ozone, not only preserve the delicate balance of life but also serve as invaluable archives of our planet’s history and windows into its potential future.
One of Earth’s most crucial invisible shields is its magnetic field. Generated by the churning movement of molten iron and nickel in the outer core, this magnetic shield extends far beyond the surface, creating a protective bubble that deflects the solar wind – a continuous stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun. This shield has profound implications for both the past and future of our planet.
Studying the Earth’s magnetic field provides scientists with a unique glimpse into the planet’s geological history. The magnetic minerals in rocks record the orientation and strength of the magnetic field at the time the rocks formed. By carefully analyzing these magnetic imprints, researchers can reconstruct past magnetic field variations, offering insights into tectonic plate movements, continental drift, and the Earth’s ancient climate.
Furthermore, the magnetic field plays a crucial role in preserving Earth’s atmosphere. Without this shield, the solar wind would strip away our protective atmospheric layers, rendering the planet barren and inhospitable. The delicate interplay between the magnetic field and the atmosphere is a testament to the intricate dance of forces that shape our planet’s history.
Beyond the magnetic shield, Earth’s atmosphere itself acts as a protective cloak, shielding life from harmful solar radiation and regulating the climate. The various layers of the atmosphere, from the troposphere to the stratosphere, hold vital clues about past climates and environmental conditions. Ice cores and sediment layers trapped in glaciers, for instance, contain a wealth of information about ancient atmospheres, revealing patterns of temperature, greenhouse gas concentrations, and even traces of human activities.
The ozone layer, situated in the stratosphere, is a specific and critical component of Earth’s invisible shield. While not completely impervious, the ozone layer absorbs the majority of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, preventing it from reaching the surface in harmful amounts. Human activities, such as the release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), have led to the depletion of this protective layer, resulting in increased UV radiation exposure and contributing to environmental issues like skin cancer and disruptions in ecosystems. Studying the ozone layer provides a unique lens through which we can understand the consequences of human actions on our planet and make informed decisions for the future.
As we contemplate Earth’s invisible shields, it becomes clear that they are not only guardians of our present but also time capsules that hold the secrets of our past. Scientific investigations into these shields offer a retrospective view of the planet’s evolution, shedding light on the intricate processes that have shaped the Earth over millions of years.
Looking to the future, these invisible shields provide crucial insights into the potential trajectories of our planet. Understanding changes in the magnetic field, atmospheric composition, and ozone layer allows scientists to model and predict the impacts of human activities, climate change, and other factors. This knowledge is essential for making informed decisions to ensure the sustainability of our planet for future generations.
In essence, Earth’s invisible shields transcend their role as protectors; they are gateways to the past and windows to the future. By unraveling the mysteries held within these shields, humanity can navigate the challenges of the present and forge a path towards a sustainable and resilient future on our dynamic and ever-evolving planet.
Earth Invisible Shield: Magnetic Field
Earth does have a magnetic field, generated by the movement of molten iron and nickel in its outer core. This magnetic field acts as a shield, protecting the planet from the solar wind – a stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun. Without this magnetic shield, solar wind could strip away the atmosphere, making the planet inhospitable. Studying Earth’s magnetic field can indeed reveal information about its geological history and processes.
Table of Contents
Earth Invisible Shield: Ozone Layer:
The Earth’s ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, acts as a shield against harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. Changes in the ozone layer can be linked to human activities, such as the release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Studying the ozone layer provides insights into the impact of human activities on the atmosphere.
Earth Invisible Shield: Atmospheric Layers
Earth‘s atmosphere itself can be considered a protective shield. The various layers of the atmosphere play crucial roles in climate regulation and weather patterns. Studying these layers helps scientists understand past climate conditions and predict future changes.
Additionally, the phrase “invisible shield” might be used metaphorically in a scientific context, and its meaning would depend on the specific research or theory being discussed.
Also Read:- Ayodhya के लिए पीएम मोदी ने कुल 15,000 करोड़ रुपये की परियोजनाओं का किया उद्घाटन